SearchTable Of Contents
Previous topicNext topicThis Page |
使用视图(Using Views)¶视图(Views)代表的就是你应用程序的用户界面。视图通常由HTML文件嵌入PHP代码组成,视图提供了为用户请求把数据输出到浏览器的任务。 Phalcon\Mvc\View 负责管理MVC应用程序中的视图层。 本组件支持文件的层次结构,这个层次结构允许常用的layout布局,以及使用控制器命名的文件夹名称,定义了各自相应的视图模板。 Integrating Views with Controllers¶Phalcon的视图组件会自动通过执行一个特定的控制器完成它的生命周期。视图组件首先要根据最后的控制器名称找到视图文件目录, 然后通过最后的Action找到视图文件名,然后输出视图内容。举例,如果一个URL请求是 http://127.0.0.1/blog/posts/show/301 , Phalcon会这样解析这个URL:
分发器会寻找一个“PostsController”和它的的Action “showAction”。一个简单的控制器文件例子: <?php
class PostsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function indexAction()
{
}
public function showAction($postId)
{
// Pass the $postId parameter to the view
$this->view->setVar("postId", $postId);
}
}
setVar方法允许我们创建视图变量,以便我们可以在视图文件中使用它们。上面的演示告诉我们如何把 $postId 这个参数绑定到视图文件上。 Phalcon\Mvc\View 使用PHP本身作为模板引擎,因此我们建议使用.phtml作为扩展名。如果视图目录是 app/views ,视图组件会自动找到以下3个视图文件。
你并不必要编写上述提到的所有三个视图文件。 Phalcon\Mvc\View 会通过视图文件的层次自动查找下一层的视图文件。如果所有三个视图文件都存在,他们将做如下处理: <!-- app/views/posts/show.phtml -->
<h3>This is show view!</h3>
<p>I have received the parameter <?php $postId ?></p>
<!-- app/views/layouts/posts.phtml -->
<h2>This is the "posts" controller layout!</h2>
<?php echo $this->getContent() ?>
<!-- app/views/index.phtml -->
<html>
<head>
<title>Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is main layout!</h1>
<?php echo $this->getContent() ?>
</body>
</html>
请注意视图文件中调用 $this->getContent() 方法的那一行。这个方法的位置决定内容在 Phalcon\Mvc\View 的层次结构中的上一个视图的哪个位置显示。上述示例将输出以下内容: 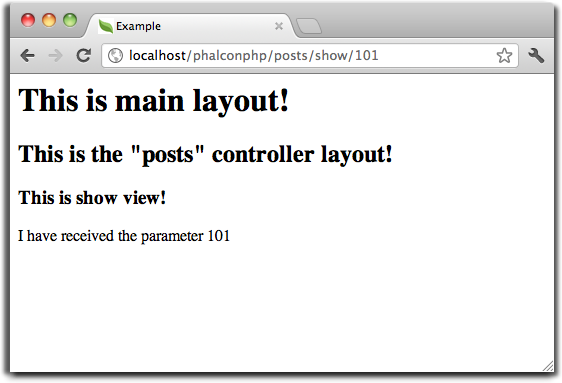
生成的HTML内容如下: <!-- app/views/index.phtml -->
<html>
<head>
<title>Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is main layout!</h1>
<!-- app/views/layouts/posts.phtml -->
<h2>This is the "posts" controller layout!</h2>
<!-- app/views/posts/show.phtml -->
<h3>This is show view!</h3>
<p>I have received the parameter 101</p>
</body>
</html>
使用模板(Using Templates)¶Templates也是视图文件的一部分,但他们是可共享的。他们作为控制器的布局文件,你必须把它们放到layouts目录下。 <?php
class PostsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function initialize()
{
$this->view->setTemplateAfter('common');
}
public function lastAction()
{
$this->flash->notice("These are the latest posts");
}
}
<!-- app/views/index.phtml -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Blog's title</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php echo $this->getContent() ?>
</body>
</html>
<!-- app/views/layouts/common.phtml -->
<ul class="menu">
<li><a href="/">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="/articles">Articles</a></li>
<li><a href="/contact">Contact us</a></li>
</ul>
<div class="content"><?php echo $this->getContent() ?></div>
<!-- app/views/layouts/posts.phtml -->
<h1>Blog Title</h1>
<?php echo $this->getContent() ?>
<!-- app/views/layouts/posts/last.phtml -->
<article>
<h2>This is a title</h2>
<p>This is the post content</p>
</article>
<article>
<h2>This is another title</h2>
<p>This is another post content</p>
</article>
最后它们将输出如下的HTML内容: <!-- app/views/index.phtml -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Blog's title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- app/views/layouts/common.phtml -->
<ul class="menu">
<li><a href="/">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="/articles">Articles</a></li>
<li><a href="/contact">Contact us</a></li>
</ul>
<div class="content">
<!-- app/views/layouts/posts.phtml -->
<h1>Blog Title</h1>
<!-- app/views/layouts/posts/last.phtml -->
<article>
<h2>This is a title</h2>
<p>This is the post content</p>
</article>
<article>
<h2>This is another title</h2>
<p>This is another post content</p>
</article>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Using Partials¶局部模板文件是另一种打破视图渲染顺序的方式,它更易于管理,且可在应用程序中重复使用。 作为局部文件的方式之一可以把它们看作是子程序,把你的视图代码分成多个组成部分,更容易被理解。例如,你可能会有这样的想法,看起来像这样: <?php $this->partial("shared/ad_banner") ?>
<h1>Robots</h1>
<p>Check out our specials for robots:</p>
...
<?php $this->partial("shared/footer") ?>
Transfer values from the controller to views¶Phalcon\Mvc\View 可以在控制器中使用视图变量($this->view)调用。你可以在控制器的Action中使用该对象的setVar()方法设置变量到视图中。 <?php
class PostsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function indexAction()
{
}
public function showAction()
{
//Pass all the posts to the views
$this->view->setVar("posts", Posts:find());
}
}
setView()的第一个参数名称是将要在视图文件中使用的,变量可以是任意类型。从字符串,整型数字,到一个更复杂的结构,如数组,集合等都可以。 <div class="post">
<?php
foreach ($posts as $post)
{
echo "<h1>", $post->title, "</h1>";
}
?>
</div>
Control Rendering Levels¶从以上可以看出,Phalcon\Mvc\View 支持视图层次结构。你可能需要在视图中控制显示的层次,PhalconMvc\View::setRenderLevel() 提供这种功能。 此方法可以从控制器或从上级视图层调用改变渲染过程。 <?php
class PostsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function indexAction()
{
}
public function findAction()
{
// This is an Ajax response so don't generate any kind of view
$this->view->setRenderLevel(\Phalcon\Mvc\View::LEVEL_NO_RENDER);
//...
}
public function showAction($postId)
{
// Shows only the view related to the action
$this->view->setRenderLevel(\Phalcon\Mvc\View::LEVEL_ACTION_VIEW);
}
}
The available render levels are:
Using models in the view layer¶应用程序中的模型是可以在视图中直接使用的,因为 Phalcon\Loader 在运行时会自动初始化它们: <div class="categories">
<?php
foreach (Catergories::find("status = 1") as $category) {
echo "<span class='category'>", $category->name, "</span>";
}
?>
</div>
虽然你可以在视图中执行模型的各种操作,如insert(),update()等,但不建议这么使用。因为它不可以在发生错误或异常的时候从一个控制流程跳转到另一个控制器。 Picking Views¶正如上面提示的,Phalcon\Mvc\Application 管理 Phalcon\Mvc\View 进行视图显示,根据相关联的最一个控制器和action来进行视图文件输出。你也可以通过 Phalcon\Mvc\View::pick() 方法改变这个显示流程: <?php
class ProductsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function listAction()
{
// Pick "views-dir/products/search" as view to render
$this->view->pick("products/search");
}
}
Caching View Fragments¶有时候,当你开发动态网站时,网页上的有一些区域是不经常更新的,他们每次都输出相同的内容。Phalcon\Mvc\View 提供了一种缓存功能,可以局部缓存,也可以缓存整个页面,以提高性能。 Phalcon\Mvc\View 集成了 Phalcon\Cache ,提供了一种更方便的方法来进行缓存操作。你可以手工设置缓存处理,或设置一个全局的缓存规则: <?php
class PostsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function showAction()
{
//Cache the view using the default settings
$this->view->cache(true);
}
public function showArticleAction()
{
// Cache this view for 1 hour
$this->view->cache(array(
"lifetime" => 3600
));
}
public function resumeAction()
{
//Cache this view for 1 day with the key "resume-cache"
$this->view->cache(
array(
"lifetime" => 86400,
"key" => "resume-cache",
)
);
}
public function downloadAction()
{
//Passing a custom service
$this->view->cache(
array(
"service" => "myCache",
"lifetime" => 86400,
"key" => "resume-cache",
)
);
}
}
当我们没有为缓存定义一个明确的KEY时,组件会自动创建一个针对视图文件名称 md5 的KEY。这样定义KEY的方式是非常不错的做法,因为这样你就可以很容易识别到每个Action与视图缓存的对应文件了。 当View组件需要缓存一些内容的时候,它将从服务容器请求cache服务。 这个服务在服务容器中的命名为”viewCache”: <?php
//Set the views cache service
$di->set('viewCache', function(){
//Cache data for one day by default
$frontCache = new Phalcon\Cache\Frontend\Output(array(
"lifetime" => 86400
));
//Memcached connection settings
$cache = new Phalcon\Cache\Backend\Memcached($frontCache, array(
"host" => "localhost",
"port" => "11211"
));
return $cache;
}, true);
当使用视图后,如果有缓存,应直接输出缓存内存进行显示,而不要使控制器再次执行获取数据。 为了实现这一目标,我们必须使用唯一的缓存KEY。首先,我们要先验证缓存的KEY是否存在或是否已过期,整个过程如下: <?php
class DownloadController extends Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function indexAction()
{
//Check if the cache with key "downloads" exists or has expired
if ($this->view->getCache()->exists('downloads')) {
//Query the latest downloads
$latest = Downloads::find(array('order' => 'created_at DESC'));
$this->view->setVar('latest', $latest);
}
//Enable the cache with the same key "downloads"
$this->view->cache(array('key' => 'downloads'));
}
}
禁用视图(Disabling the view)¶如果您的控制器不产生任何输出,您可以禁用视图组件,避免不必要的处理: <?php
class UsersController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function closeSessionAction()
{
//Disable the view
$this->view->disable();
//The same
$this->view->setRenderLevel(Phalcon\Mvc\View::LEVEL_NO_RENDER);
}
}
模板引擎(Template Engines)¶模板引擎可帮助前端设计人员无需使用复杂的语法就可以创建视图。Phalcon自身包含了一个强大快速的模板引擎 Volt 。 此外, Phalcon\Mvc\View 还允许你使用其他的模板引擎替代PHP或Volt. 使用不同的模板引擎,通常需要复杂的外部PHP库,用于解析模板文件。这通常会增加你的应用程序的资源数量。 如果你要使用一个外部模板引擎, Phalcon\Mvc\View 会提供完全相同的视图层次结构,它同样可以在模板中访问API。 该组件使用适配器,这可以帮助外部模板引擎在Phalcon中是统一的,让我们来看看如何整合其他模板引擎的。 创建自己的模板引擎适配器(Creating your own Template Engine Adapter)¶有很多的模板引擎,比如常用的Smarty,你可能需要集成或自己创建一个。使用外部模板引擎的第一步就是要为它创建一个适配器。 模板引擎适配器是一个类,它用作 Phalcon\Mvc\View 与模板引擎集成工作的一个桥梁。通常只需要实现 __construct() 和 render() 两个方法。构造方法用于传入 Phalcon\Mvc\View 的实际对象和服务容器(DI). render()方法接收两个参数,第一个为视图文件的绝对路径,第二个参数是通过 $this->view->setVar() 设置模板变量。 <?php
class MyTemplateAdapter extends \Phalcon\Mvc\View\Engine
{
/**
* Adapter constructor
*
* @param \Phalcon\Mvc\View $view
* @param \Phalcon\DI $di
*/
public function __construct($view, $di)
{
//Initiliaze here the adapter
parent::__construct($view, $di);
}
/**
* Renders a view using the template engine
*
* @param string $path
* @param array $params
*/
public function render($path, $params)
{
// Access view
$view = $this->_view;
// Access options
$options = $this->_options;
//Render the view
}
}
更换模板引擎(Changing the Template Engine)¶你可以使用以下方式在控制器中替换或添加一个模板引擎: <?php
class PostsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function indexAction()
{
// Set the engine
$this->view->registerEngines(
array(
".my-html" => "MyTemplateAdapter"
)
);
}
public function showAction()
{
// Using more than one template engine
$this->view->registerEngines(
array(
".my-html" => 'MyTemplateAdapter'
".phtml" => 'Phalcon\Mvc\View\Engine\Php'
)
);
}
}
你还可以完全替换模板引擎,或同时使用多个模板引擎都是可以的。 Phalcon\Mvc\View::registerEngines() 方法接收一个数组参数。数组的KEY是扩展名,值为模板名。扩展名称不要一样,以区别使用的是哪个模板引擎。 如果使用多个模板引擎,同时设置的扩展名称一样,那么 Phalcon\Mvc\View 将只显示第一个。 如果你想实现在应用程序中每个请求都使用一个或一组模板引擎,你可以注册view服务到服务容器: <?php
//Setting up the view component
$di->set('view', function() {
$view = new \Phalcon\Mvc\View();
$view->setViewsDir('../app/views/');
$view->registerEngines(
array(
".my-html" => 'MyTemplateAdapter'
)
);
return $view;
});
为了更好的理解如何创建一个模板引擎适配器,让我们集成两个众所周知的模板:Mustache 和 Twig. Using Mustache¶Mustache 是一个logic-less的模板引擎,可用于多平台多语言。PHP的实现版本在这里 this Github repository 。 你需要在使用模板适配器前手工加载Mustache的库文件。可以使用autoload的方式,也可以使用include包含文件的方式。 <?php
require "path/to/Mustache/Autoloader.php";
Mustache_Autoloader::register();
Mustache的适配器看起来像这样: <?php
/**
* Adapter to use Mustache library as templating engine
*/
class My_Mustache_Adapter extends \Phalcon\Mvc\View\Engine
{
protected $_mustache;
protected $_params;
public function __construct(Phalcon\Mvc\View $view, Phalcon\DI $di)
{
$this->_mustache = new Mustache_Engine();
parent::__construct($view, $di);
}
public function render($path, $params)
{
if (!isset($params['content'])) {
$params['content'] = $this->_view->getContent();
}
$this->_view->setContent($this->_mustache->render(file_get_contents($path), $params));
}
}
现在,在控制中你需要把模板引擎替换成 Mustache 适配器,如果你的控制器中的所有Action都使用此模板引擎,你可以在initialize()方法中注册它。 <?php
class PostsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller implements Phalcon\Mvc\View\EngineInterface
{
public function initialize()
{
// Changing PHP engine by Mustache
$this->view->registerEngines(
array(".mhtml" => "My_Mustache_Adapter")
);
}
public function showAction()
{
$this->view->setVar("showPost", true);
$this->view->setVar("title", "some title");
$this->view->setVar("body", "a cool content");
}
}
相对的模板文件 (views-dir/posts/show.mhtml) 将使用 Mustache 语法进行解析。 {{#showPost}}
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<p>{{body}}</p>
{{/showPost}}
此外,正如上面看到的,你必须在视图文件中调用方法 $this->getContent() 以包含内容。在Moustache中,它是这么使用的: <div class="some-menu">
<!-- the menu -->
</div>
<div class="some-main-content">
{{content}}
</div>
Using Twig¶Twig 是最近比较流行的PHP模板引擎。 你在使用模板引擎适配器前同样需要手工加载Twig的库文件,使用autoloader加载可以按如下方式实现: <?php
require "path/to/Twig/Autoloader.php";
Twig_Autoloader::register();
Twig模板引擎适配器看起来像这样: <?php
/**
* Adapter to use Twig library as templating engine
*/
class My_Twig_Adapter extends \Phalcon\Mvc\View\Engine implements Phalcon\Mvc\View\EngineInterface
{
protected $_twig;
public function __construct(Phalcon\Mvc\View $view, Phalcon\DI $di)
{
$loader = new Twig_Loader_Filesystem($view->getViewsDir());
$this->_twig = new Twig_Environment($loader);
parent::__construct($view, $di);
}
public function render($path, $params)
{
$view = $this->_view;
if (!isset($params['content'])) {
$params['content'] = $view->getContent();
}
if (!isset($params['view'])) {
$params['view'] = $view;
}
$relativePath = str_replace($view->getViewsDir(), '', $path);
$this->_view->setContent($this->_twig->render($relativePath, $params));
}
}
从上面可以看出,你需要替换默认的模板引擎或让它和其他的模板引擎一起工作。 <?php
class PostsController extends \Phalcon\Mvc\Controller
{
public function initialize()
{
// Changing PHP engine by Twig
$this->view->registerEngines(
array(".twig" => "Twig")
);
}
public function showAction()
{
$this->view->setVar("showPost", true);
$this->view->setVar("title", "some title");
$this->view->setVar("body", "a cool content");
}
}
在这种情况下,相关的视图文件为views-dir/posts/show.twig,这个文件里面写的是包含twig语法的代码。 {{% if showPost %}}
<h1>{{ title }}</h1>
<p>{{ body }}</p>
{{% endif %}}
然后需要把内容包含进来,这里使用变量”content”,和Mustache的方式是一样的: <div class="some-messages">
{{ content }}
</div>
Using Smarty¶Smarty 是另一个PHP模板引擎,它负责应用逻辑和视图的分隔。 你需要在使用适配器之前手工加载库文件,这么做: <?php
require_once 'Smarty3/Smarty.class.php';
Smarty模板引擎适配器看起来是这个样子的: <?php
class SmartyEngine extends \Phalcon\Mvc\View\Engine implements Phalcon\Mvc\View\EngineInterface
{
protected $_smarty;
protected $_params;
public function __construct(Phalcon\Mvc\View $view, Phalcon\DI $di)
{
$this->_smarty = new Smarty();
$this->_smarty->template_dir = '.';
$this->_smarty->compile_dir = SMARTY_DIR . 'templates_c';
$this->_smarty->config_dir = SMARTY_DIR . 'configs';
$this->_smarty->cache_dir = SMARTY_DIR . 'cache';
$this->_smarty->caching = false;
$this->_smarty->debugging = true;
parent::__construct($view, $di);
}
public function render($path, $params)
{
if (!isset($params['content'])) {
$params['content'] = $this->_view->getContent();
}
foreach($params as $key => $value){
$this->_smarty->assign($key, $value);
}
$this->_view->setContent($this->_smarty->fetch($path));
}
}
在视图中使用服务(Injecting services in View)¶每个视图文件中都包含 Phalcon\DI\Injectable 的实例对象,方便的提供了访问服务容器的功能。 下面的例子演示了如何在框架约定下写一个 jQuery ajax request 。视图文件中包含”url”这个服务,你可以直接使用它: <script type="text/javascript">
$.ajax({
url: "<?php echo $this->url->get("cities/get") ?>"
})
.done(function() {
alert("Done!");
});
</script>
Stand-Alone Component¶在Phalcon中,一般使用 glue 组件使一些松散的组件连接在一起相互工作,形成一个full-stack框架开发环境,但是你也可以单独使用 Phalcon\Mvc\View : <?php
$view = new \Phalcon\Mvc\View();
$view->setViewsDir("../app/views/");
// Passing variables to the views, these will be created as local variables
$view->setVar("someProducts", $products);
$view->setVar("someFeatureEnabled", true);
//Start the output buffering
$view->start();
//Render all the view hierarchy related to the view products/list.phtml
$view->render("products", "list");
//Finish the output buffering
$view->finish();
echo $view->getContent();
View Events¶Phalcon\Mvc\View 可以将事件发送到 EventsManager 。事件通过”view”来触发。一些返回布尔值false的事件可以被停止,支持下列一些事件:
下面的示例演示如何将事件监听器绑定到组件: <?php
$di->set('view', function() {
//Create an event manager
$eventsManager = new Phalcon\Events\Manager();
//Attach a listener for type "view"
$eventsManager->attach("view", function($event, $view) {
echo $event->getType(), ' - ', $view->getActiveRenderPath(), PHP_EOL;
});
$view = new \Phalcon\Mvc\View();
$view->setViewsDir("../app/views/");
//Bind the eventsManager to the view component
$view->setEventsManager($eventManagers);
return $view;
});
下面的示例展示了如何创建一个插件,用来clean/repair 在渲染过程中的HTML代码。我们使用 Tidy 来演示: <?php
class TidyPlugin
{
public function afterRender($event, $view)
{
$tidyConfig = array(
'clean' => true,
'output-xhtml' => true,
'show-body-only' => true,
'wrap' => 0,
);
$tidy = tidy_parse_string($view->getContent(), $tidyConfig, 'UTF8');
$tidy->cleanRepair();
$view->setContent((string) $tidy);
}
}
//Attach the plugin as a listener
$eventsManager->attach("view:afterRender", new TidyPlugin());
|
